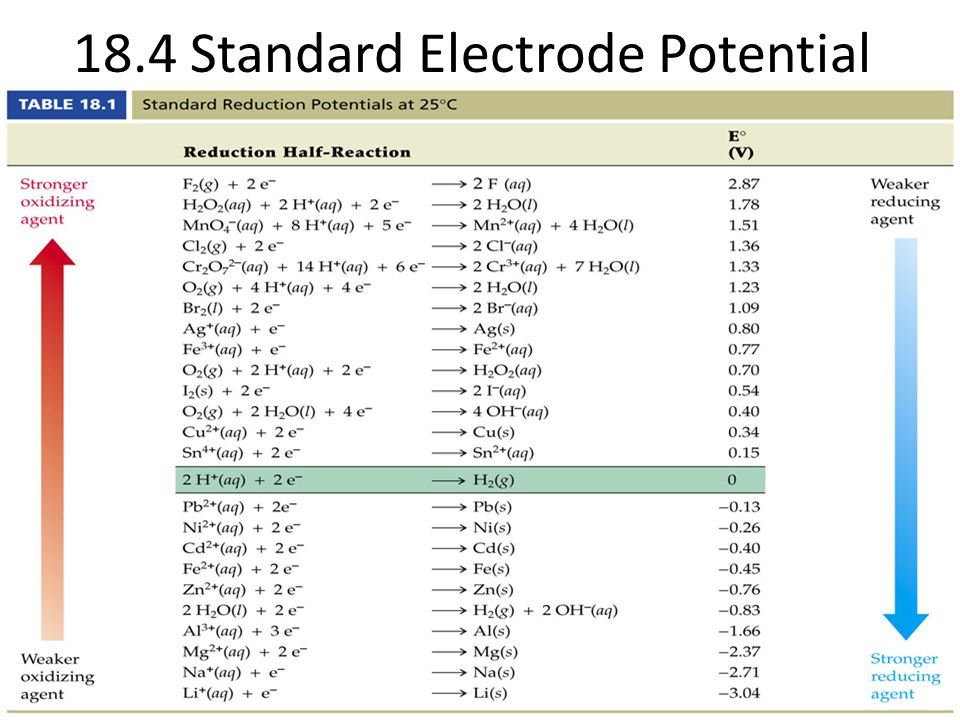
Standard Cell Potential Chart . The values of electrode potentials are customarily. 2h2o (l) → h2 (g) + o2 (g) (under acidic conditions where the standard reduction potential of oxygen is +1.23 v) free expert solution 79% (270 ratings)
Gibbs Free Energy Changes And Standard Reduction Potentials At 25 • C... | Download Table from www.researchgate.net
Mg(s) + 2ag+(aq) mg2+(aq) + 2ag(s) e∘ cell = 0.7996 v − (−2.372 v) = 3.172 v mg ( s) + 2 ag + ( a q) mg 2 + ( a q) + 2 ag ( s) e cell ∘ = 0.7996 v − ( − 2.372 v) = 3.172 v key concepts and summary What is the standard electrode potential? Recommendations are made for standard potentials involving select inorganic 47 radicals in aqueous solution at 25 °c.
Gibbs Free Energy Changes And Standard Reduction Potentials At 25 • C... | Download Table The overall cell potential can be calculated by using the equation. Electron free energy chart of standard reduction potentials; Calculate the standard cell potential at 25 °c. Table of standard reduction potentials.
Source: www.youtube.com Electron free energy chart of standard reduction potentials; Standard reduction potentials are potentials for electrodes in which all components are in a standard state at 25ºc, with ion concentrations of 1 m and gas pressures of one atm. See chemical ideas 9.2 redox reactions and electrode potentials for details. To understand standard reduction potentials and to calculate the emf of.
Source: www.quora.com These recommendations are based on a critical and 48 thorough literature review and also by performing derivations from various literature reports. H 2 (−2.23 v), na + (−2.71 v), li + (−3.05 v)). Ag + + e − ag. > the first step is to determine the cell potential at its standard state — concentrations of 1 mol/l and pressures.
Source: chem.libretexts.org Zn 2+ has a standard reduction potential of −0.76 v and thus can be oxidized by any other electrode whose standard reduction potential is greater than −0.76 v (e.g. 41 rows standard potentials at 25°c. Standard reduction potentials are potentials for electrodes in which all components are in a standard state at 25ºc, with ion concentrations of 1 m and.
Source: grade12uchemistry.weebly.com The values of electrode potentials are customarily. Reduction reaction takes place at the cathode,. Significance of standard electrode potential. E ° (v) ag + + e − ag. Recommendations are made for standard potentials involving select inorganic 47 radicals in aqueous solution at 25 °c.
Source: www.chegg.com Significance of standard electrode potential. Supporting this predication by calculating the standard cell potential for this reaction gives e ° cell = e ° cathode − e ° anode = e ° fe (ii) − e ° cr = −0.447 v − −0.744 v = +0.297 v the positive value for the standard cell potential indicates the process is spontaneous.
Source: www.researchgate.net The overall cell potential can be calculated by using the equation. See chemical ideas 9.2 redox reactions and electrode potentials for details. Agcl + e − ag + cl −. Electron free energy chart of standard reduction potentials; The symbol ‘e o cell ’ represents the standard electrode potential of a cell.
Source: www.pdfprof.com Ag + + e − ag. 305 rows the data values of standard electrode potentials (e°) are given in the table below, in. To understand standard reduction potentials and to calculate the emf of a voltaic cell working definitions:. Supporting this predication by calculating the standard cell potential for this reaction gives e ° cell = e ° cathode −.
Source: Agcl + e − ag + cl −. When a reactant oxidizes and reduces itself; Agcl + e − ag + cl −. In this lesson we look into the factors that determine the value of a standard cell potential. 6 electrical work and galvanic cells;
Source: www.corrosion-doctors.org Determine the new cell potential resulting from the changed conditions. The overall cell potential can be calculated by using the equation. Recommendations are made for standard potentials involving select inorganic 47 radicals in aqueous solution at 25 °c. Table of standard reduction potentials. See chemical ideas 9.2 redox reactions and electrode potentials for details.
Source: jolieblogz.blogspot.com Determine the new cell potential resulting from the changed conditions. These recommendations are based on a critical and 48 thorough literature review and also by performing derivations from various literature reports. Ap20 appendix h standard reduction potentials appendix h standard reduction potentials* reaction e (volts) de/dt (mv/k) aluminum al3 3e tal(s) 1.677 0.533 alcl2 3e tal(s) cl 1.802 alf 3e.
Source: www.researchgate.net Standard reduction (electrode) potentials at 25 o c; To determine the cell potential when the conditions are other than standard state (concentrations not 1 molar and/or pressures not 1 atmosphere): When a reactant oxidizes and reduces itself; Indicate whether the reaction would be spontaneous or not. Table of standard reduction potentials.
Source: www.chegg.com Reduction reaction takes place at the cathode,. In an electrochemical cell, an electric potential is created between two dissimilar metals. List the known values and plan the problem. Determine q, the reaction quotient. Calculate the standard cell potential at 25 °c.
Source: chemistsk027.blogspot.com Zn 2+ has a standard reduction potential of −0.76 v and thus can be oxidized by any other electrode whose standard reduction potential is greater than −0.76 v (e.g. To determine the cell potential when the conditions are other than standard state (concentrations not 1 molar and/or pressures not 1 atmosphere): The overall cell potential can be calculated by using.
Source: www.flinnsci.com > the first step is to determine the cell potential at its standard state — concentrations of 1 mol/l and pressures of. The overall cell potential can be calculated by using the equation. Determine the new cell potential resulting from the changed conditions. To understand standard reduction potentials and to calculate the emf of a voltaic cell working definitions:. Zn(s).
Source: www.researchgate.net Agcl + e − ag + cl −. Table of standard reduction potentials. Using the standard reduction potential chart in your textbook, find e°cell for the following balanced reaction. Calculation of cell potential (eo cell) to calculate cell potential: Determine the new cell potential resulting from the changed conditions.
Source: ch302.cm.utexas.edu The difference in potential energy between the anode and cathode is known as the cell potential in a voltaic cell. Agcl + e − ag + cl −. In this lesson we look into the factors that determine the value of a standard cell potential. The values of electrode potentials are customarily. Agcl + e − ag + cl −.
Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com H 2 (−2.23 v), na + (−2.71 v), li + (−3.05 v)). It is a reduction potential). To determine the cell potential when the conditions are other than standard state (concentrations not 1 molar and/or pressures not 1 atmosphere): Using the standard reduction potential chart in your textbook, find e°cell for the following balanced reaction. 41 rows standard potentials at.
Source: www.youtube.com 6 electrical work and galvanic cells; See chemical ideas 9.2 redox reactions and electrode potentials for details. To determine the cell potential when the conditions are other than standard state (concentrations not 1 molar and/or pressures not 1 atmosphere): The symbol ‘e o cell ’ represents the standard electrode potential of a cell. Indicate whether the reaction would be spontaneous.
Source: sites.google.com > the first step is to determine the cell potential at its standard state — concentrations of 1 mol/l and pressures of. In an electrochemical cell, an electric potential is created between two dissimilar metals. In an electrochemical cell, an electric potential is created between two dissimilar metals. Zn 2+ has a standard reduction potential of −0.76 v and thus.
Source: slideplayer.com Determine q, the reaction quotient. Calculate the standard cell potential at 25 °c. 49 the recommended data are summarized in tables of standard potentials, gibbs energies of 50. In an electrochemical cell, an electric potential is created between two dissimilar metals. Ag + + e − ag.