I-Mr Chart . The center line is the average of all moving ranges. When you change an unstable process, you can't accurately assess the effect of the changes.
I-Mr Chart - Six Sigma Study Guide from sixsigmastudyguide.com
The control limits on the i chart, which are set at a distance of 3 standard deviations above and below the center line, show the amount of variation that is expected in the individual sample values. These charts are used to verify process control before assessing capability such as cpk, ppk, cp, pp, or cpm. Determining whether a process is stable and ready to be improved.
I-Mr Chart - Six Sigma Study Guide Conforms with ansi/asqc b1, b2, b3 1996. It allows such a process to be assessed for stability both in terms of central tendency as well as variation. Points that fail minitab's tests are marked with a red symbol on the mr chart. The moving range (mr) chart shows variability between one.
Source: www.youtube.com The moving range chart plots the moving ranges of the subgroup means. For n=2 observations (moving range is calculated from two samples, the present minus the previous value) d 4 = 3.267. The center line is an estimate of the process average. There are a few commonly used charts to assess process control. Conforms with ansi/asqc b1, b2, b3 1996.
Source: www.researchoptimus.com The individual (x) chart displays individual measurements. The constants are used as follows: (however, research has shown that for normally distributed processes, when a special causes is detected. There are times when you might want to just look at the variation between consecutive samples. Conforms with ansi/asqc b1, b2, b3 1996.
Source: www.isixsigma.com Used to determine if a process is stable and predictable, it creates a picture of how the system changes over time. Thanks & regards, prasad v. Below is a table of control chart constants used to calculate control limits. The individual (x) chart displays individual measurements. K = number of data points.
Source: www.qimacros.com It allows such a process to be assessed for stability both in terms of central tendency as well as variation. Obtain the acumulated value of the absolute diference between one data point and the previous point 2. (however, research has shown that for normally distributed processes, when a special causes is detected. There are times when you might want to.
Source: www.youtube.com Below is a table of control chart constants used to calculate control limits. Please confirm and clarify my doubts, and do the required changes. Determining whether a process is stable and ready to be improved. The moving range chart plots the moving ranges of the subgroup means. Thanks & regards, prasad v.
Source: sixsigmastudyguide.com Used to determine if a process is stable and predictable, it creates a picture of how the system changes over time. The center line is an estimate of the process average. The moving range chart (the lower chart in the figure) shows the absolute difference between two consecutive. Here we can tell minitab to store the standard deviation in the.
Source: www.qimacros.com The constants are used as follows: The individual (x) chart displays individual measurements. Qi macros will do the math and draw the charts for you and turn unstable points or conditions red. Determining whether a process is stable and ready to be improved. They consist of two separate charts;
Source: sixsigmastudyguide.com They consist of two separate charts; Below is a table of control chart constants used to calculate control limits. For imr or xmr charts (the same) you can do it very simple in excel, just: The moving range (mr) chart shows variability between one. The moving range chart plots the moving ranges of the subgroup means.
Source: www.researchgate.net The individual x chart (the upper chart in this figure) illustrates an actual individual reading or measurement taken for quality control sampling purposes. I think, there may be some typographical mistake, i.e. When you change an unstable process, you can't accurately assess the effect of the changes. Qi macros will do the math and draw the charts for you and.
Source: www.six-sigma-material.com (however, research has shown that for normally distributed processes, when a special causes is detected. The moving range chart plots the moving ranges of the subgroup means. K = number of data points. Please confirm and clarify my doubts, and do the required changes. The individual (x) chart displays individual measurements.
Source: support.minitab.com There are a few commonly used charts to assess process control. Used to determine if a process is stable and predictable, it creates a picture of how the system changes over time. These charts are used to verify process control before assessing capability such as cpk, ppk, cp, pp, or cpm. Thanks & regards, prasad v. When you change an.
Source: www.researchoptimus.com (however, research has shown that for normally distributed processes, when a special causes is detected. They consist of two separate charts; For imr or xmr charts (the same) you can do it very simple in excel, just: I & mr charts are control charts designed for tracking single points of continuous data. These charts are used to verify process control.
Source: blog.minitab.com K = number of data points. Obtain the acumulated value of the absolute diference between one data point and the previous point 2. The moving range (mr) chart shows variability between one. They consist of two separate charts; For n=2 observations (moving range is calculated from two samples, the present minus the previous value) d 4 = 3.267.
Source: www.researchgate.net Here we can tell minitab to store the standard deviation in the worksheet when we create the chart: It is typical to use individual observations instead of rational subgroups when there is no basis for forming subgroups, when there is a long interval between observations becoming available, when testing is destructive or expensive, or for. I & mr charts are.
Source: www.qimacros.com It is typical to use individual observations instead of rational subgroups when there is no basis for forming subgroups, when there is a long interval between observations becoming available, when testing is destructive or expensive, or for. For example, suppose you company is tracking accounts. Select two or more columns of data. The center line is an estimate of the.
Source: support.minitab.com There are times when you might want to just look at the variation between consecutive samples. Qi macros will do the math and draw the charts for you and turn unstable points or conditions red. Here we can tell minitab to store the standard deviation in the worksheet when we create the chart: Always look at moving range chart first..
Source: support.minitab.com Thanks & regards, prasad v. The xbar chart plots the mean of the each subgroup. Admin — december 7, 2012. Select two or more columns of data. The moving range chart plots the moving ranges of the subgroup means.
Source: www.youtube.com When you change an unstable process, you can't accurately assess the effect of the changes. (however, research has shown that for normally distributed processes, when a special causes is detected. They consist of two separate charts; The xbar chart plots the mean of the each subgroup. Conforms with ansi/asqc b1, b2, b3 1996.
Source: www.qimacros.com Below is a table of control chart constants used to calculate control limits. The moving range chart plots the moving ranges of the subgroup means. I & mr charts are control charts designed for tracking single points of continuous data. The control limits on the i chart, which are set at a distance of 3 standard deviations above and below.
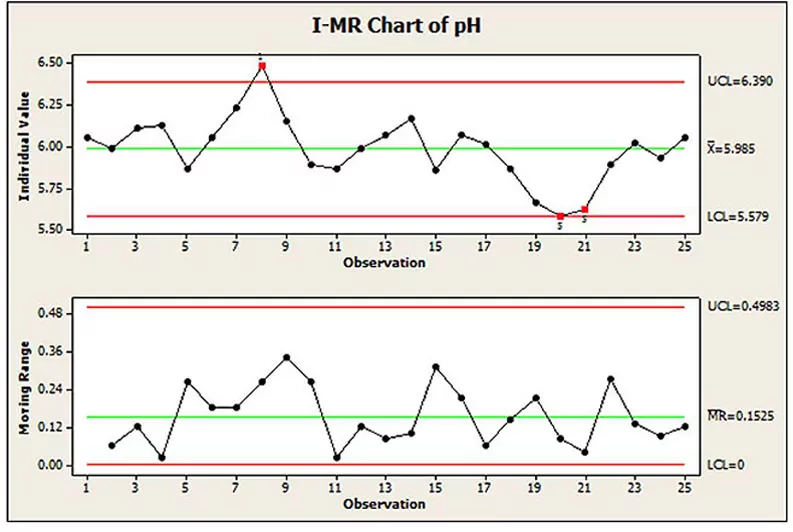
Source: www.six-sigma-material.com Points that fail minitab's tests are marked with a red symbol on the mr chart. The center line is an estimate of the process average. Select two or more columns of data. In this mr chart, the lower and upper control limits are 0 and 0.4983, and none of the individual observations fall outside those limits.the points. The individual (x).